Skin-whitening active ingredients in cosmetics: Classification, mechanisms, and safety considerations
22/01/2026

The demand for skin-whitening ingredients has become increasingly popular in modern skincare. However, many people still understand “skin-whitening” in a subjective way—expecting rapid results and a visibly lighter skin tone in a short period of time. This misconception often leads to choosing the wrong active ingredients, using them incorrectly, and exposing the skin to potential risks.
From a dermatological science perspective, skin whitening is not simply about making the skin look brighter; it is directly related to the process of melanin formation and the skin’s biological regulatory mechanisms. Without a proper understanding of this nature, users may easily trade long-term skin health for short-term results.
This article from Nguyen Ba Chemical will help you gain a clear understanding of what skin-whitening ingredients are, how they work, how to distinguish them from skin-brightening agents, how to evaluate their safety, and how to choose the most suitable options for different skin conditions.
What are skin-whitening active ingredients?
Definition from a dermatological-cosmetic perspective
In cosmetic science, skin-whitening active ingredients are a group of compounds capable of interfering with the biosynthesis or expression of melanin, thereby reducing dark pigmentation and improving overall skin tone.
This concept is fundamentally different from the common, non-scientific understanding of “fast whitening,” which is often associated with immediate results but lacks biological control. A true skin-whitening ingredient must act selectively, be safe, and provide sustainable effects with long-term use.
What determines skin color?
Human skin color is primarily determined by melanin, a pigment produced by melanocyte cells. The amount of melanin is not only influenced by genetics but also affected by several other factors, such as:
- UV radiation stimulating increased melanin production.
- Skin inflammation or damage.
- Aging processes and reduced cellular regeneration.
Therefore, to intervene in skin whitening safely, it is essential to understand these underlying mechanisms before choosing the appropriate products.

Mechanisms of action of skin-whitening active ingredients
This section is a key factor that helps readers distinguish truly effective products from solutions that are merely marketing-driven.
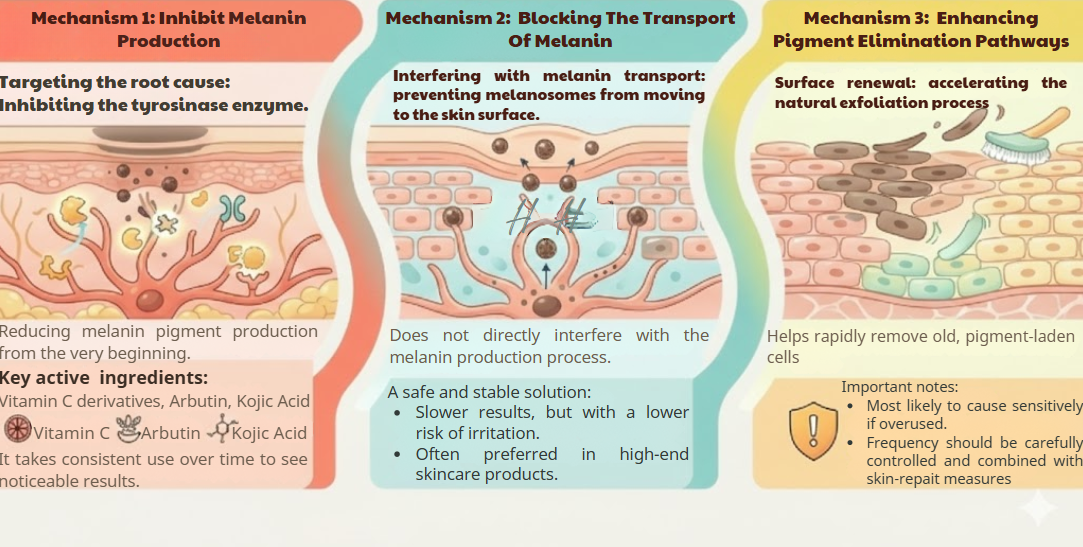
Inhibition of melanin synthesis
Many skin-whitening active ingredients work by inhibiting the enzyme tyrosinase, which plays a central role in the melanin synthesis pathway.
Common groups of ingredients include vitamin C derivatives, arbutin, kojic acid, and standardized bio-extracts. This mechanism helps reduce pigmentation at its source, but it requires time for visible results to appear.
Inhibition of melanin transport to the skin surface
Some active ingredients do not directly interfere with melanin production but instead disrupt the transport of melanosomes to the epidermal layers.
This mechanism tends to produce slower results, but it is more stable and less irritating. For this reason, many high-end skincare products favor this approach to ensure long-term safety.
Acceleration of the removal of pigment-containing keratinocytes
Certain active ingredients promote exfoliation, helping to remove melanin-containing cells more quickly. However, this is also the mechanism most likely to cause skin sensitivity if overused or applied at high concentrations.
The use of this group requires strict control of application frequency and should be combined with appropriate skin-repair and barrier-supporting measures.
Classification of common skin-whitening active ingredients
In modern cosmetics, skin-whitening active ingredients are mainly classified based on how they affect the formation and expression of melanin. This classification helps clarify the concept of physiological skin brightening and avoids confusion with unsafe skin-bleaching methods. Each group of skin-whitening ingredients has distinct mechanisms, levels of effectiveness, and applications in cosmetic formulations.
Tyrosinase-inhibiting skin-whitening active ingredients
This group acts directly on tyrosinase, the key enzyme in the melanin synthesis process. When the activity of this enzyme is inhibited, melanin production gradually decreases, resulting in brighter and more even-toned skin over time.
Typical active ingredients in this group include:
- Arbutin and its derivatives.
- Kojic acid and kojic derivatives.
These ingredients are commonly used in intensive skin-whitening products and require careful concentration control to ensure skin tolerance.
Vitamin C and Vitamin C–derived skin-whitening active ingredients
Vitamin C is one of the most popular skin-whitening ingredient groups due to its dual benefits of skin brightening and antioxidant protection. These activities help reduce melanin formation while protecting the skin from environmental damage.
In cosmetic formulations, Vitamin C is mainly used in two forms:
- Ascorbic acid (pure Vitamin C).
- More stable Vitamin C derivatives.
Choosing the appropriate form of Vitamin C helps balance skin-whitening efficacy with product stability.

Melanin transport–regulating skin-whitening active ingredients
Unlike direct inhibitors, this group of skin-whitening ingredients acts on the transport of melanin from melanocytes to the epidermal layers. As a result, the skin retains its natural protective mechanisms while the surface appears brighter and more even-toned.
Niacinamide is a representative ingredient of this group. In addition to regulating melanin transfer, it also helps restore the skin barrier and improve uneven skin tone.
Skin-renewal–supporting and indirectly brightening active ingredients
Some skin-whitening ingredients do not act directly on melanin but improve skin tone by promoting cellular renewal. As old keratinized cells are shed, newly regenerated skin appears brighter and smoother.
This group commonly includes:
- AHA (Alpha Hydroxy Acids).
- PHA (Poly Hydroxy Acids).
When using these ingredients, sun protection should be incorporated to maintain long-term brightening effects.
New-generation skin-whitening active ingredients with high safety profiles
In addition to single active ingredients, modern cosmetics increasingly favor multi-mechanism skin-whitening complexes that target multiple stages of melanin formation and expression simultaneously. This approach helps improve overall skin brightness while maintaining long-term safety.
-
Hepawhite™ NAA
Hepawhite™ NAA is a multi-mechanism skin-whitening complex that combines Niacinamide, Alpha-Arbutin, Nonapeptide-1, Ascorbyl Glucoside, and HEPES. By simultaneously acting on melanin synthesis, deposition, and expression, Hepawhite™ NAA helps brighten the skin, improve hyperpigmentation, and enhance overall skin tone uniformity.
This active is suitable for intensive skin-whitening formulations that aim to improve overall skin tone rather than deliver instant whitening effects.
-
Hepawhite™ NAG
Hepawhite™ NAG is a next-generation, physiologically oriented skin-whitening complex containing Niacinamide, Nonapeptide-1, Ascorbyl Glucoside, and HEPES. It helps regulate melanin formation, reduce pigment accumulation, and support sustainable skin brightening.
Thanks to its gentle formulation base, Hepawhite™ NAG is suitable for daily-use skin-whitening products and sensitive skin.
-
Starwhite™
Starwhite™ is a notable example, with Glabridin extracted from licorice root as its key component. This active helps inhibit tyrosinase, supports skin brightening, and also provides antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and skin-repair benefits. Starwhite™ is commonly used in natural cosmetic formulations or products designed for sensitive skin.
Skin-whitening active ingredients derived from natural extracts
Botanical extracts are a commonly used group of skin-whitening ingredients in natural and botanical-based cosmetic lines. These extracts help improve skin tone in a gentle and safe manner, making them suitable for sensitive skin.
Some commonly used extracts include:
- Licorice extract.
- Centella asiatica extract.
- Green tea extract.
This group is known for its high safety profile, but it requires consistent, long-term use to achieve visible results.

Active ingredients that are not considered safe skin-whitening agents
Some substances have been mistakenly perceived as skin-whitening ingredients but are not recommended for use in cosmetics due to their potential risks to the skin. Identifying this group helps both consumers and manufacturers avoid selecting inappropriate raw materials. This category includes substances that are prohibited in cosmetics under current cosmetic regulations.
How to choose suitable skin-whitening active ingredients
Choosing the right skin-whitening active ingredients should not be based on the promise of rapid whitening. Instead, it requires a comprehensive evaluation of the mechanism of action, safety profile, and the skin’s ability to tolerate the ingredient. A suitable skin-whitening active should effectively improve skin tone while preserving the skin barrier during long-term use.
Selecting skin-whitening actives based on skin condition
A common mistake is choosing a skin-whitening ingredient first and then trying to “fit” it to the skin. In reality, skin condition is the key factor in determining which active ingredients are appropriate. Weak, sensitive, or recovering skin requires whitening ingredients with regulatory and gentle mechanisms, whereas resilient skin can better tolerate more direct-acting actives.
Skipping proper skin assessment may cause even widely regarded “safe” whitening ingredients to trigger irritation or counterproductive results.
Selecting based on whitening mechanisms
Not all skin-whitening ingredients work through the same mechanisms. Understanding these mechanisms helps prevent misuse and reduces the risk of skin irritation. Some ingredients are suitable for overall skin brightening, while others should be used specifically to support the reduction of dark spots or hyperpigmentation.
Common skin-whitening mechanisms include:
- Inhibition of melanin synthesis.
- Regulation of melanin transport.
- Support of skin cell renewal.

Prioritize skin-whitening active ingredients approved for cosmetic use
A skin-whitening ingredient is only truly suitable when it is approved for use in cosmetics and applied within safe concentration limits. Ingredients that deliver rapid whitening effects but are unapproved or restricted often pose significant risks to the skin when used long term.
For manufacturers, selecting skin-whitening actives must be accompanied by complete technical documentation to ensure legal compliance and sustainable product circulation in the market.
Consider compatibility within cosmetic formulations
Sustainable skin-whitening results often come from a well-balanced combination of multiple whitening active groups. However, not all ingredients are compatible in terms of pH, stability, or mechanisms of action.
Before selection, it is essential to consider:
- Compatibility between active ingredients.
- Stability of whitening actives within the formulation.
- Impact on product texture and skin feel.
Choose skin-whitening actives from reputable suppliers
Ultimately, skin-whitening ingredients can only perform effectively when the raw materials meet quality standards. Clear origin, consistent quality specifications, and transparent technical documentation are indispensable factors.
For cosmetic manufacturers, partnering with reputable suppliers not only ensures product performance but also minimizes risks related to quality control and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
Understanding skin-whitening ingredients correctly is the key to safe and effective skincare. Sustainable skin whitening does not come from instant solutions, but from choosing active ingredients that align with the skin’s biological mechanisms.


